Before you stand up to give a presentation, you probably set goals for yourself, right? Things like present with confidence. Get through without too many “ums.” Or make good eye contact. But have you ever set goals for your audience before giving a presentation?
Audience goals keep you focused on the exact change you are hoping to accomplish. It might be to help the audience understand a new policy, to join a work team, or to purchase a product. Best-selling author Dr. Stephen Covey says you should “begin with the end in mind.” In other words, you should know what you hope to accomplish before you start writing your presentation. And that’s what we are talking about today.
If you are preparing a presentation in hopes that it will be effective, you need to understand how humans learn and then set specific learning goals for your audience. So let’s talk about different levels of learning and how to leverage these in your presentations.
Bloom’s Taxonomy
In 1956, Benjamin S. Bloom created a hierarchy of learning that is known as Bloom’s Taxonomy. Bloom’s guide helps us understand the different levels of learning. In 2000 Anderson and Krathwohl updated Bloom’s original language as shown in the table below. Bloom’s taxonomy moves from the lowest level of learning, which is remembering, to the highest level of learning found in creating.
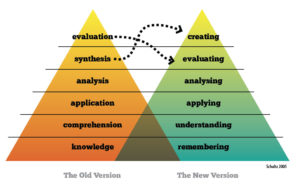
As a presenter, this hierarchy can help you set appropriate goals for your presentation. Before doing that though, let’s learn a little bit more about each level. The Teaching and Educational Institute of The University of Queensland in Australia defines each level like this:
- knowledge: can recall of specific items
- comprehension: can recall, but can do a little more (e.g. paraphrase, define, discuss to some extent)
- application: can take information of an abstract nature and use it in concrete situations
- analysis: can break down a communication into its constituent parts, revealing the relationships among them
- evaluation: can make judgements about the value of materials or methods
- synthesis: can pull together many disorganized elements or parts so as to form a whole
Looking at those levels, ask yourself, what is it that I want my audience to be able to do at the end of my presentation? If you simply want them to remember the key terms or points, a presentation focused on remembering is fine. But if you want them to be able to apply the information you are presenting, you’ll need to aim a little higher.
Let’s discuss some specific ways to accomplish each learning level goal in your presentations. Keep in mind that they are cumulative; they build upon each other. So if your ultimate goal is to get your audience to the application level, you need to also use the tips in the lower levels that come before application. Let’s get started.
If your goal for your audience is remembering:
Keep the main terms in your presentation the same. If you tell your audience you are going to cover “how caffeine affects your brain and body,” don’t switch that to “cerebral and physical effects of caffeine” later in your presentation. Certain words become anchor points for your audience. They are listening for them. And they use them to orient themselves within the presentation, so don’t switch them up.
Also, repeat the terms or points that you want the audience to retain at least 3 times. Once in the introduction, once in the body of your message, and once as you are reviewing in your conclusion.
If your goal for your audience is understanding:
Move beyond definition to illustrations and examples that connect with your audience. Words don’t mean much until they connect to something we know. Connection is the start of understanding. Here’s how to make that happen. In their 2019 article, “Unleashing the Power of Examples,” Dr. Ken Alford and Dr. Tyler Griffin share a story originally told by Dr. Kim B. Clark of an elementary teacher who taught his fourth graders about German theologian Martin Luther. Following his lesson, the students took a quiz, but they bombed the quiz. They answered the questions as if the quiz was about Martin Luther King Jr., the American civil rights activist and leader.
The next time the teacher taught this same lesson on Martin Luther, he started his presentation like this: “How many of you know who Martin Luther King, Jr. was?” When all of the students raised their hands, he asked, “Do any of you know why his parents gave him the name of Martin Luther?” As Alford and Griffin write, “He then shared the same information he had presented to the first group, but the students heard his lesson differently because it built on information they already understood.” The second group of students passed their quizzes easily. The first level of learning, remembering, is aimed at basic memorization. But the second level, understanding, connects new information with what the audience already knows.
If your goal for your audience is applying:
The above example gets partly into application because the students were asked to take a quiz on the information. That shows that they were able to apply what they had learned. But I’m guessing you aren’t planning to give your audience members a quiz following your presentation. Instead, you can achieve this level of learning by asking your audience to provide some examples of their own. Once you’ve explained a point or concept, ask for feedback either by opening the floor for them to share examples or by asking them to share examples in small groups.
If your goal for your audience is analyzing:
At this stage of learning, you should start to view your audience members not as students, but as decision makers. In order for your audience make the best decision, they have to be able to analyze your ideas, so you need to help them understand all the component parts. Say for example you are giving a sales pitch. Helping them analyze might mean that your presentation needs to cover the history of your product, the motivating factor for its creation, the ways in which it solves problems for other customers, data on its cost effectiveness, statistics on how it compares to its competitors, etc. This stage illustrates why Bloom’s taxonomy can be so helpful for setting your audience presentation goals. If your audience doesn’t need to analyze or make decisions, you can leave out some of this more detailed and granular information.
If your goal for your audience is evaluating:
With this level of learning, you are helping your audience form opinions about your ideas. You are asking them to assign value and judge something to be right/wrong, good/bad, helpful/not helpful, true/false, and so on. One of the main goals of information presentation is to help your audience get to the place where they judge your content to be worthy of their time, attention, money, respect, or support. In order to do this, you need to show how the information you’ve presented affects their daily lives in a positive way. Without this explicit connection, the audience can too easily dismiss your presentation as irrelevant.
If your goal for your audience is creating:
The highest level of learning is synthesizing or creating. Remember that all the levels of learning build upon each other. So in order to get to this last and highest step, you need to move the audience through the other levels first. It could be that your presentation goal is to get your audience to take what they’ve learned from you and use it to create new ideas, new products, or new policies of their own.
In these cases, you need to focus on inspiration and motivation. Don’t waste time on things the audience already knows. Instead, spend your energy actually getting them to act. For example, if you are launching a recycling initiative at your workplace, don’t bog them down with recycling stats and why recycling is good for the planet. You may touch on this briefly, but don’t spend too much time on it because the audience already accepts that recycling is a worthy cause. Instead, figure out how to convince them to actually start acting on this initiative and creating new initiatives of their own that coincide with those of the company.
When you know what your goal is for your audience members, you can start to balance your presentation content accordingly. What do you need to spend the most time on? Is there anything your audience doesn’t need to know that you can take out? What do you need to accomplish first before moving on to higher levels of learning? Bloom’s taxonomy helps you ask the right questions so you develop the right presentation to get the right results.
Ready to take your presentation to the next level? Find out how Ethos3 can help.